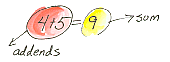Mathematical "A" Words
Mathematical "A" Words*Dictionary Alert
absolute value The absolute value of a number is the distance that number is from zero. The absolute value of a positive number or zero is that number. The absolute value of a negative number is the opposite of that number, and the absolute value of zero is zero which is neither positive or negative.
Ex:
|3| = 3, and |-3| = 3, |0| = 0 .
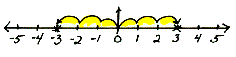
Both 3 and -3 are 3 jumps away from zero, so they have the same absolute value of 3.
The absolute value bars | |, act as grouping symbols. You must simplify any expressions within these bars before finding the final absolute value.
Ex: |3-7| = |-4| = 4.
acre A unit of area often used to measure plots of land. One acre is equivalent to exactly 43,560 square feet, or 4,840 square yards, or 1/640 of a square mile, or about 4,047 square meters.
acute
angle
An angle whose measure is between 0° and 90º. We like to think of them
as the "cute" skinny angles.
Addition Property of Equality If a = b, then a + c = b + c. Add the same thing to both sides of an equation and you still have an equation.
Ex:
3 = 12/4
7 + 3 = 12/4 + 7
10 = 10
additive identity The number zero. When you add zero to any number, you do not change its identity, thus the name, additive identity.
Additive Identity Property of Zero For any number n: n + 0 = n. If you add zero to any other number, you do not change its identity.
Additive Inverse The number, which when added to a number, gives a sum of 0. The additive inverse of n is denoted -n. Also called opposite.
Add-opp Property of Subtraction For any numbers a and b: a - b = a + -b. In words, subtracting b is the same as adding the opposite of b.
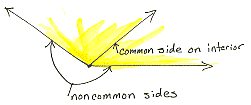
adjacent
angles
Two nonstraight and nonzero angles with a common side interior to the
angle formed by the noncommon sides.
adjacent sides In a polygon, two sides with an endpoint in common.
adjacent vertices In a polygon, endpoints of a side.
algebraic expression An expression that contains a variable alone or with numbers and operation symbols.
Ex:
y
3xy
4x + 2
algorithm A sequence of steps that leads to a desired result.
alternate
exterior angles
Angles formed by two lines and a transversal whose interiors are not
between the two lines and are on different sides of the transversal.
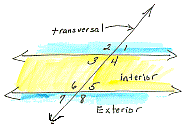 |
Angles one and seven are alternate exterior angles as are angles two and eight. When the two lines cut by the transversal are parallel, the alternate exterior angles will be congruent. |
alternate
interior angles
Angles formed by two lines cut by a transversal. They are between
the two lines and on alternate sides of the transversal.
 |
Angles three and five are alternate interior angles as are angles four and six. When the two lines cut by the transversal are parallel, the alternate interior angles will be congruent. |
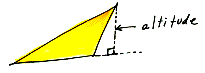
altitude
In a triangle or trapezoid, the segment from a vertex perpendicular to
the line containing the opposite side;

also, the length of that segment. In a prism or cylinder, the distance
between the bases. In a pyramid or cone, the length of a segment from
the vertex perpendicular to the plane of the base. Also called height.
altitude
of a triangle
The perpendicular distance from any vertex of a triangle to the side opposite
that vertex. Also called height.
analytic geometry A geometry in which points are represented by coordinates and where algebraic methods of reasoning are utilized.
angle
The union of two rays with the same endpoint.
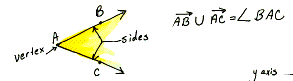
The rays are the sides and the common endpoint is called the vertex. There
are many types of angles. See the definitions for zero angle, right angle,
straight angle, acute angle, obtuse angle, reflex angle.
angle bisector The ray with points in the interior of an angle that forms two angles of equal measure with the sides of the angle.
angle of depression An angle measured from the horizontal plane downward from an observer's eye to a given point below the plane.
angle of elevation An angle measured from the horizontal plane upward from an observer's eye to a given point above the plane.
angle of inclination See angle of elevation.
antecedent The "if" clause of a conditional. Also called hypothesis.
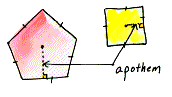
apothem
The perpendicular segment from the center of a regular n-gon to one of
its sides.
arc
A path from one point (node) of a network to another point (its endpoints
or vertices).
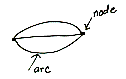
A part of a circle connecting two points (its endpoints) on the circle.
area Measure of the space inside a two-dimensional figure. Area is measured in square units.
Area Model for Multiplication The area of a rectangle with length l and width w is l times w or a = lw.
arthmetic mean The result of adding the n numbers in a data set and dividing the sum by n. Also called the average or mean.
Associative
Property of Addition For
any numbers a, b, and c:
( a + b) + c = a + ( b + c ) = a + b + c. The positions
of the numbers do not change, the placement of the grouping symbols changes.
Ex:
(1+2)+3 = 1+(2+3)
3+3 = 1+5
6=6
Associative
Property of Multiplication
For any numbers a, b, and c:
a( bc ) = ( ab )c = abc. The positions of the numbers do not change,
the placement of the grouping symbols changes.
Ex:
3(4x5) = (3x4)5
3(20) = 12(5)
60 = 60
automatic drawer Computer software or calculator that enables geometric figures to be constructed from input by the user. Click HERE to get one we recommend.
auxiliary figure A figure that is added to a given figure, often to aid in completing proofs.
average A number representing a set of other numbers determined by taking the sum of those numbers and dividing by the number of them. Also called mean or arithmetic mean.
axis
A line of reference in a coordinate system. Plural: axes.
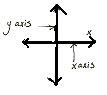
axis of a cone The line through the cone's vertex and the center of its base.
Home | About
Us | Algebra| Dictionary | Games | Geometry | Gym | Humor | Lab | Magic | Natural Math | PreAlgebra | Resources | Teachers Only | Toolbox | Treasures | Videos | Wonders | Writings |
Copyright © 1999-2020 themathlab.com